Monthly Minimum Wage
- In 2024, the minimum wage is KHR 1,069,900 per month.
- There may be differences among different industries.
Overtime Pay and Maximum Working Hours
- Standard working hours: 8 hours per day, 40 hours per week (Monday – Friday).
- A Monday – Saturday work system can be implemented, with a maximum of 48 hours per week.
- Overtime pay (working beyond standard working hours is considered overtime):
- Overtime on normal working days: 150% of normal wage.
- Night – time overtime (22:00–05:00) and work on weekly rest days: 200% of normal wage.
- Night shift or rotating shift (22:00–05:00): 130% of normal wage.
- Work on public holidays: 100% of normal wage (plus the wage for that holiday).
- The maximum overtime per day is 2 hours. Overtime pay will be applied for any overtime beyond this limit.
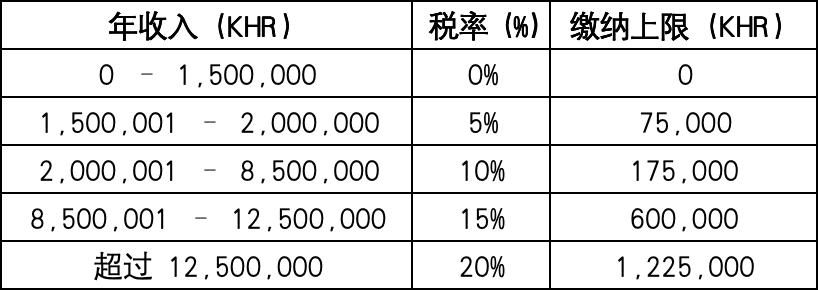
Personal Income Tax
- Cambodia does not levy personal income tax, but employees need to pay relevant contributions and payroll taxes based on their wages.
- The payroll tax rate ranges from 0% to 20%, with a payment cap for each income bracket.
Statutory Holidays
- Employees are entitled to 18 working days of paid annual leave per year.
- Annual leave is accrued monthly, at a rate of 1.5 days per month.
- Employees can enjoy annual leave after completing one consecutive year of work.
- In addition, employees can get additional annual leave days for every three consecutive years of work.
- Employers usually also provide special leave (Special Leave) for 7 days.
National Public Holidays
Cambodia has 15 national public holidays every year, totaling 21 – 22 days. The main public holidays include:
- International New Year’s Day
- Day of the Victory over Genocide
- International Women’s Day
- Cambodian New Year
- International Labour Day
- Visaka Bochea Day
- Royal Ploughing Ceremony
- King Norodom Sihamoni’s Birthday
- Queen Mother Norodom Monineath Sihanouk’s Birthday
- Constitution Day
- Pchum Ben Day
- Day of Mourning for the Late King Norodom Sihanouk
- Coronation Day of King Norodom Sihamoni
- National Independence Day
- Water Festival
Other Types of Leave
Maternity Leave
- Eligible employees: Those who have worked continuously for at least 1 year.
- Leave duration: 90 days of paid maternity leave.
- Wage treatment: 50% of the wage during the leave period, paid by the employer.
Paternity Leave
- Statutory paid days: 5 days, which must be taken immediately after the child’s birth.
- Common practice: Employers usually provide an additional 7 – 15 days of paid leave.
- Wage treatment: 100% of the wage during the leave period, paid by the employer.
Parental Leave
- Cambodian law does not stipulate parental leave.
- Employees can enjoy maternity leave and paternity leave.
Sick Leave
- Employees can enjoy a maximum of 12 days of paid sick leave per year.
- For continuous sick leave exceeding 3 days, a sick – leave certificate from an authorized doctor is required.
Employment Contracts
- Contract types: Employment contracts in Cambodia can be either fixed – term contracts (Fixed – term) or indefinite – term contracts (Indefinite – term).
- The contract must clearly specify the employee’s salary, benefits, termination clauses, and the amount of salary and other compensation.
- A contract lacking the above main contents will be considered invalid.
- The main information that the contract should contain:
- Contract type
- Employee’s passport information
- Contract start date
- Contract end date (for fixed – term contracts)
- Position/Job title
- Salary and other benefits
- Job description
- Termination conditions
Probation Period
- Minimum probation period: 30 days.
- Maximum probation period: 90 days.
- The probation period applies to the initial assessment stage clearly stipulated in the contract, used to evaluate whether the employee meets the job requirements.
Employer Costs
- Employer costs are usually 5.40% of the employee’s salary, with the following breakdown:
- Pension fund: 2%
- Occupational risk contribution: 0.8%
- Medical insurance contribution: 2.6%
- Note: The above are estimated values for reference only. For complete fee and terms information, please contact the sales team for an official quote.
Termination of Employment (Legal Requirements and Best Practices)
Notice Period
- Legal Requirements
- During the probation period: No notice period is required.
- After the probation period:
- Indefinite – term contracts: The notice period ranges from 7 days to 3 months depending on the length of service.
- Fixed – term contracts: The notice period ranges from 10 to 15 days depending on the contract term.
- Payment in lieu of notice: Allowed.
- Garden Leave: Allowed.
- Local Best Practices
- During the probation period: 7 – day notice period.
- After the probation period: In accordance with legal requirements.
- Payment in lieu of notice: Common practice.
- Garden Leave: Common practice.
Termination of Employment Contract Due to Employee Misconduct (Termination With Cause)
- Definition: Employers are allowed to terminate the employment contract due to employee misconduct.
- Reasons for termination:
- An employee can be terminated for the following reasons: violating Article 8 (Guarantees and Conflicts of Interest), Article 11 (Confidentiality and Non – disclosure Obligations), Article 12 (Non – disparagement and Media Agreement), or Article 14 (Intellectual Property and Moral Rights) of the employment contract, or any other applicable clauses in the employer’s policy; having serious misconduct as determined by law or the employer’s standards.
- Compliance requirements:
- For serious misconduct, if the employer fails to take termination measures within 7 days after learning of the incident, it is considered to have waived the right to terminate, unless the employer can prove that the behavior is indeed serious misconduct.
- Special provisions for female employees: If an employment contract is terminated within one year after the employee gives birth, it needs to be approved by the labor inspector (in accordance with Guide No. 015/25).
- Statutory notice period:
- Indefinite – term contracts (Indefinite contracts):
- < 6 months: 7 days.
- 6 months to 2 years: 15 days.
- 2 to 5 years: 1 month.
- 5 to 10 years: 2 months.
- 10 years: 3 months.
- Fixed – term contracts (Fixed – term contracts):
- Contract term of 6 – 12 months: 10 days.
- Contract term of 12 – 24 months: 25 days.
- Indefinite – term contracts (Indefinite contracts):
- Severance pay: There is no legal requirement for severance pay when terminating the contract due to employee misconduct.
- Severance regulations for other situations:
- Indefinite – term contracts: During the notice period, employees are entitled to 2 days of paid job – seeking leave per week (written notice is required); seniority payment: 15 days of salary and other benefits per year of service, paid in two installments per year: 7.5 days in June and 7.5 days in December.
- Fixed – term contracts: At least 5% of the total contract salary and benefits.
- Final payment: The employee’s due salary and benefits should be paid within 48 hours after termination.
- Notice method: Written notice stating the reason for termination and providing evidence of misconduct. It can be delivered in person or sent by registered mail (confirmation of receipt by the employee is required).
Termination of Employment Contract Due to Redundancy or Other Business Reasons (Termination for Redundancy or Other Business Reasons)
- Definition: Employers are allowed to terminate the employment contract due to business redundancy or other reasonable business reasons.
- Reasons for termination:
- Mass lay – offs: Caused by a reduction in business activities or expected internal restructuring of the enterprise.
- Force majeure situations: Such as the enterprise encountering events beyond reasonable control (natural disasters, wars, etc.).
- Compliance requirements:
- In the case of mass lay – offs, the employer needs to follow the following procedures:
- Determine the order of lay – offs based on the employees’ professional abilities, years of service, and family burdens.
- Must notify the employee representatives in writing and seek their suggestions, especially regarding advance notice and measures to reduce the impact of lay – offs.
- Priority order for lay – offs: First, lay off employees with lower professional abilities, then those with shorter service years. The service years of married employees are increased by 1 year, and 1 year is added for each dependent child.
- Laid – off employees have the right to priority re – employment for the same position within 2 years. Employees need to notify the employer of any address changes. If there is a vacancy, the employer needs to notify the employee by registered mail, and the employee should report for work within 1 week after receiving the letter.
- The labor inspector needs to be informed of the entire lay – off process. At the request of the employee representatives, the inspector can convene relevant parties to discuss the impact of lay – offs and mitigation measures. In special cases, the Minister of Labor can issue a Prakas (ministerial order) to suspend lay – offs for no more than 30 days to help all parties find solutions, and such suspensions can be repeated a maximum of once.
- In the case of mass lay – offs, the employer needs to follow the following procedures:
- Statutory notice period:
- Indefinite – term contracts (Indefinite contracts):
- < 6 months: 7 days.
- 6 months to 2 years: 15 days.
- 2 to 5 years: 1 month.
- 5 to 10 years: 2 months.
- 10 years: 3 months.
- Fixed – term contracts (Fixed – term contracts):
- Contract term of 6 – 12 months: 10 days.
- Contract term of 12 – 24 months: 15 days.
- Indefinite – term contracts (Indefinite contracts):
- Notes:
- In force majeure situations, no notice period is required for both types of contracts, unless: the enterprise is closed by the public sector; disasters (such as floods, earthquakes, wars) cause long – term inability to resume work.
- If the enterprise is closed due to the employer’s death, employees are entitled to compensation equivalent to the notice period.
- Severance pay:
- In the case of mass lay – offs:
- Service period of 6 – 12 months: 7 days of salary and benefits.
- Service period exceeding 12 months: 15 days of salary and benefits per year of service, with a maximum cumulative limit of 6 months.
- In force majeure situations:
- Indefinite – term contracts: Entitled to 2 days of paid job – seeking leave per week during the notice period (written notice is required); seniority payment: 15 days of salary and benefits per year of service, paid in two installments per year, 7.5 days in June and 7.5 days in December.
- Fixed – term contracts: At least 5% of the total contract salary and benefits.
- In the case of mass lay – offs:
- Final payment: The employee’s due salary and benefits should be paid within 48 hours after termination.
- Notice method: Provide written notice of termination stating the reason for termination. It can be delivered in person or sent by registered mail (confirmation of receipt by the employee is required).
Employee Resignation (Resignation)
- Definition: Employees can voluntarily resign and terminate the employment contract at any time.
- Reason for termination: No specific reason needs to be provided.
- Compliance requirements: Employees need to submit a written resignation letter by email and sign it themselves.
- Statutory notice period:
- Indefinite – term contracts (Indefinite Contracts):
- Service period < 6 months: 7 days.
- Service period from 6 months to 2 years: 15 days.
- Service period from 2 to 5 years: 1 month.
- Service period from 5 to 10 years: 2 months.
- Service period > 10 years: 3 months.
- Fixed – term contracts (Fixed – term Contracts):
- Contract term of 6 to 12 months: 10 days.
- Contract term of 12 to 24 months: 15 days.
- Indefinite – term contracts (Indefinite Contracts):
- Severance pay: No legal requirement.
- Final payment: The employee’s due salary and benefits should be paid within 48 hours after the contract is terminated.
Mutual Termination of Employment Relationship (Mutual Termination)
- Definition: Employers and employees can terminate the employment contract through mutual agreement for any reason.
- Common scenarios:
- The employee may be controversial or prone to litigation.
- The employee cannot be terminated for cause or due to redundancy/other business reasons.
- The employee has reached a termination agreement with the employer through negotiation.
- Compliance requirements: For mutual termination, a separate termination agreement needs to be signed, and it must be jointly signed by the employer and the employee in the presence of a labor inspector.
- Statutory notice period: As agreed through mutual negotiation.
- Severance pay:
- Must be paid, and the amount must be higher than the legal minimum standard.
- Usually, an additional 1 – 2 months’ salary is paid on top of the legal minimum standard as compensation for waiving future liabilities.
- Final payment: The employee’s due salary and benefits should be paid within 48 hours after the contract is terminated.
Termination of Employment Relationship During Probation Period (Termination During Probation Period)
- Definition: During the probation period, employers or employees can terminate the employment relationship at any time.
- Reasons for termination:
- There is no legal requirement, but common reasons may include: poor work performance, improper behavior, frequent lateness or absenteeism without reason.
- Compliance requirements: No legal requirement.
- Statutory notice period: No legal requirement.
- Severance pay: No legal requirement.
- Final payment: The employee’s due salary and benefits should be paid within 48 hours after the contract is terminated.
- Notice method: Provide written notice of termination stating the reason for termination. The notice can be delivered in person or sent by registered mail (confirmation of receipt by the employee is required).
